Services
Comprehensive Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) Management: Evidence-Based Approaches
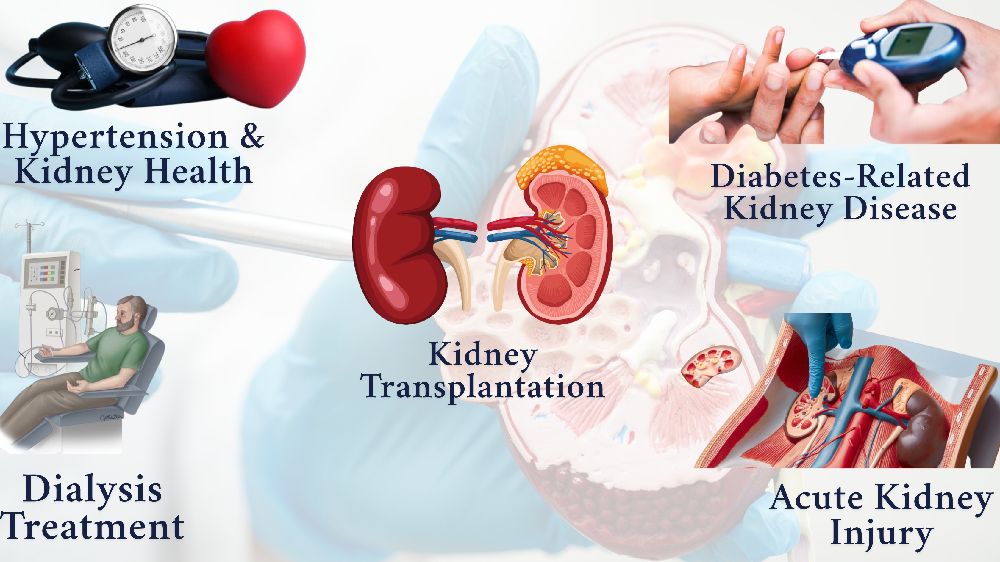
🩺 Hypertension & Kidney Health: Optimizing Blood Pressure to Safeguard Renal Function
-
Implementing a target systolic blood pressure (SBP) of <120 mm Hg is recommended for adults with CKD, when tolerated, to slow disease progression and reduce cardiovascular risk.
-
First-line pharmacological interventions include ACE inhibitors or angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs), particularly in patients with elevated albuminuria or reduced eGFR.
🩺 Dialysis Treatment: Advanced Hemodialysis & Peritoneal Dialysis Options
-
Personalized dialysis plans are essential, considering factors like residual kidney function, comorbidities, and patient preferences.
-
Regular monitoring and adjustment of dialysis prescriptions are crucial to optimize patient outcomes and minimize complications.
🩺 Kidney Transplantation: Comprehensive Pre- and Post-Operative Care
-
Thorough evaluation of transplant candidates, including immunological assessments and psychosocial evaluations, is vital.
-
Post-transplant care focuses on immunosuppressive therapy management, infection prevention, and monitoring for graft function.
🩺 Diabetes-Related Kidney Disease: Preventive Strategies for Diabetic Nephropathy
-
Aggressive glycemic control and blood pressure management are paramount to prevent or slow the progression of diabetic nephropathy.
-
Regular screening for albuminuria and eGFR is recommended for early detection and intervention.
🩺 Acute Kidney Injury (AKI): Rapid Diagnosis and Intervention Protocols
-
Early identification and management of AKI are critical to prevent progression to chronic kidney disease.
-
Treatment strategies include optimizing fluid balance, avoiding nephrotoxic agents, and considering renal replacement therapy when indicated.

.png)